A sealant can significantly improve the effect of visceral surgery; it can not only reduce intraoperative blood loss, but also reduce postoperative complications such as secondary hemorrhage and tissue adhesion, which are essential in surgical operations. However, the sealant currently used for in vivo hemostasis cannot address the needs in the modern aging society. The main challenges are its safeness, easiness of preparation and removal, and price. The commercial synthetic sealants are mainly made up of PEG, for example the 4-arm PEG hydrogel based on the ammonolysis reaction. Those sealants have advantages of high strength, strong adhesion and economic price, but the disadvantage is that they cannot be quickly degraded and can easily cause foreign body reaction in the wound that leads to healing delay.
In order to overcome the limitations of the existing PEG hydrogels, a new PEG sealant based on multi-arm PEG Succinimidyl Succinate (amide bond) has been jointly developed by Institute of Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Science and the General Hospital of People's Liberation Army.
The in vitro experiments show that SS glue has a better hemostatic effect than the previously developed SG and gauze. SS can quickly stanch the bleeding on the wound as well as prevent the adhesion issue after the operation. In contrast, SG and gauze both have different degree of postoperative adhesion when they are used for hemostasis. However, this is not the case for SS, as it is able to stop bleeding effectively even for patients taking anticoagulants, which cannot be achieved by the widely used fibrin glue.
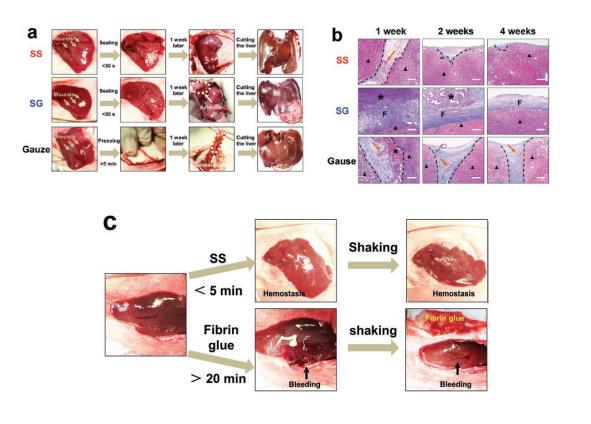
The researchers compare the hemostatic effects of SS, SG and gauze on wounds. Among them, SS and SG can achieve rapid wound hemostasis, while gauze is much slower. And after a week of hemostasis, both SG and gauze have different degrees of adhesion while SS does not have such side effects. It indicates that SS not only can stop bleeding, but also acts as a physical barrier to prevent the wound from adhering to the surrounding tissues during the healing process (Figure a). Figure b compares the healing situation of wounds at different times after surgery. Figure c compares the separate hemostatic effects of SS and fibrin glue used in the wounds of a New Zealand white rabbit with anticoagulants. SS has a better hemostatic effect than fibrin glue in terms of speed and stability. The author further uses SS to perform the hemostasis experiment on a large wound surface (diameter: 25mm, depth: 10mm). Even if a coagulant is used, SS can effectively stop bleeding after a certain period of time.
[1] Bu Y , Zhang L , Sun G , et al. Tetra㏄EG Based Hydrogel Sealants for In Vivo Visceral Hemostasis[J]. Advanced Materials, 2019, 31(28):1901580.1-1901580.10.
If there is any copyright infringement, please contact us and we will remove the content at the first time.
Sinopeg provide various NW poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) products: 2KDa, 5KDa, 10KDa, 20KDa, etc.
Products:
Linear Monofunctional PEGs
Linear Bifunctional PEGs
Linear Heterofunctional PEGs
Branched PEGs
Multi-Arm Functional PEGs
Functionally Grafted PEGs





















