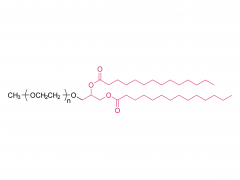
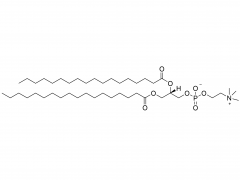
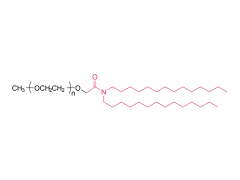
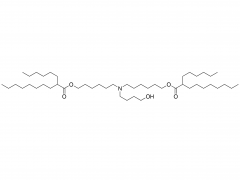
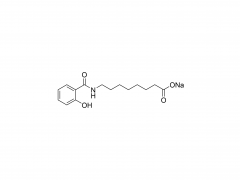
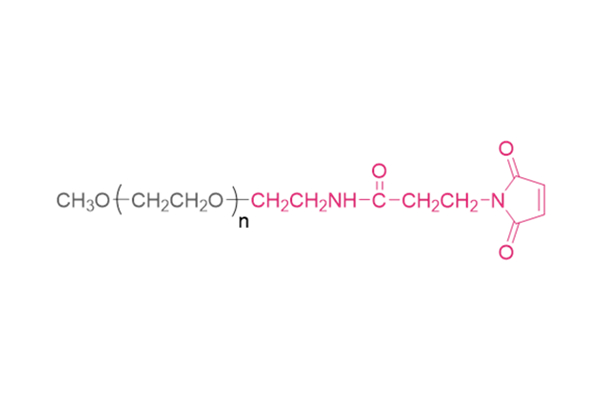
Osteoporosis is defined as a systemic and metabolic bone disease, which is characterized by a decrease in bone mass per unit volume and deterioration of the microstructure of bone tissue, thereby increasing bone fragility and susceptibility to fracture. With the increase in the proportion of elderly populations in the world, and in consequence the number of postmenopausal woman, sarcopenia and osteoporosis are important public health issues. Alendronate (ALN) is a kind of bisphosphonate, which is the most widely used medication in the treatment of skeletal disorders such as osteoporosis, due to its significant pharmacological effect of inhibition on bone resorption. However, the poor permeability exhibit extremely low bioavailability after oral administration (less than 1%). Furthermore, to avoid serious side effects caused by drug-food interactions, patients were instructed to take the medication orally in the morning at least 30 min before breakfast with abundant water and on an empty stomach after an overnight fast, and to remain upright for at least 30 min after dosing. To overcome the limitations of conventional treatments and provide better patient compliance, researchers from the Chinese Academy of Sciences and Zhengzhou University have jointly developed a minimally invasive procedures system for long-term injectable drug delivery, which is effective for clinical osteoporosis therapy (Scheme 1). They introduced PEGylated ALN (PEG-ALN) prodrug into the tetra-PEG hydrogel network, which limits the release rate of ALN because the PEG-ALN polymer does not move easily and freely in the 4 arm PEG hydrogel network, thus achieving slow drug release and local drug delivery, avoiding the serious side effects of systemic administration. 1. Dawei Li, Jin Zhou, Mingming Zhang, Yuanzheng Ma, Yanyu Yang,* Xue Han* and Xing Wang*. Long-term delivery of alendronate through injectable tetra-PEG hydrogel to promote osteoporosis therapy. Biomater. Sci. 2020, 8, 3138–3146.
View More