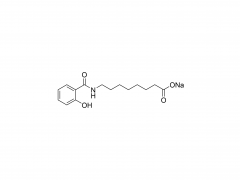
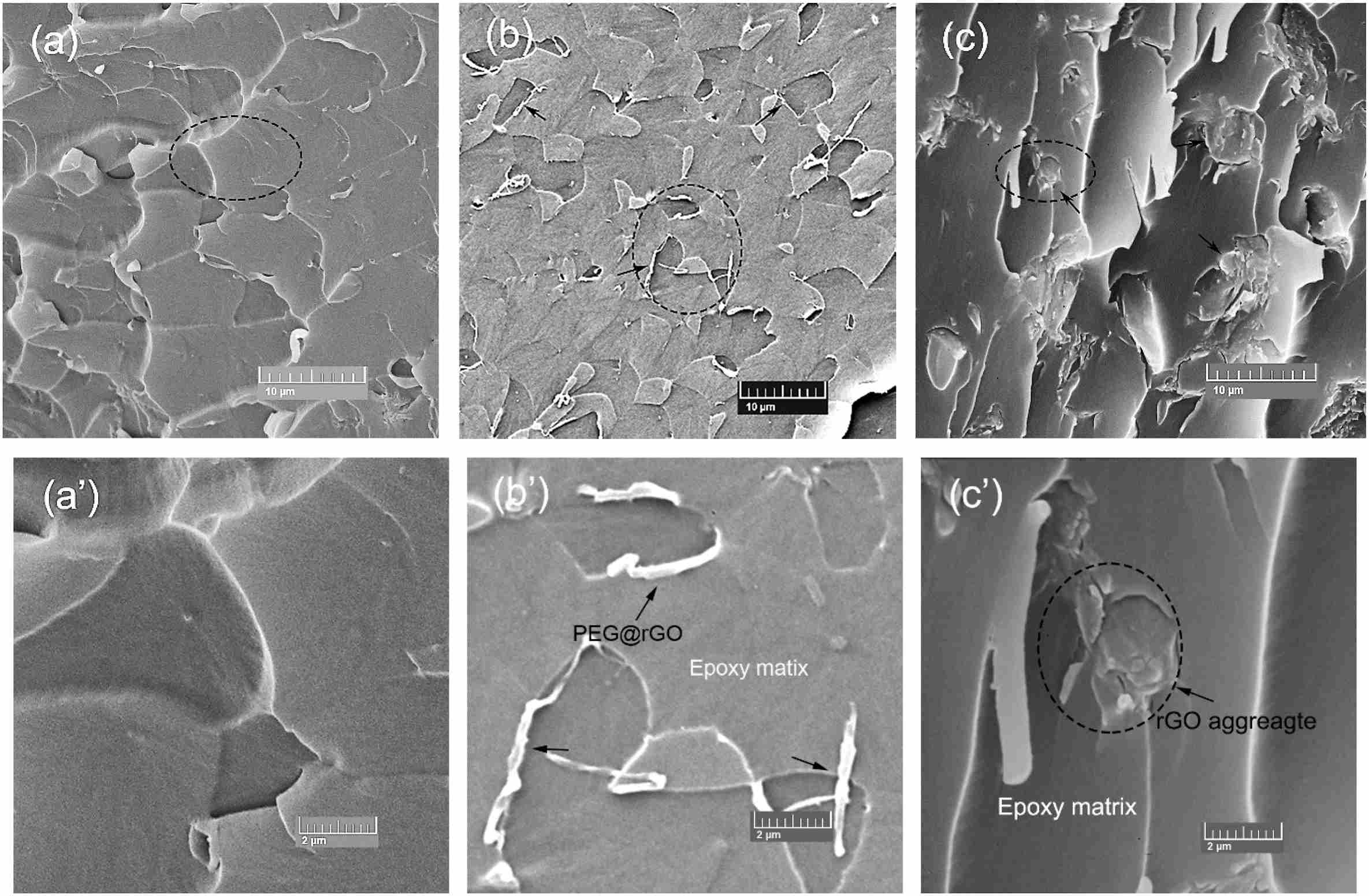
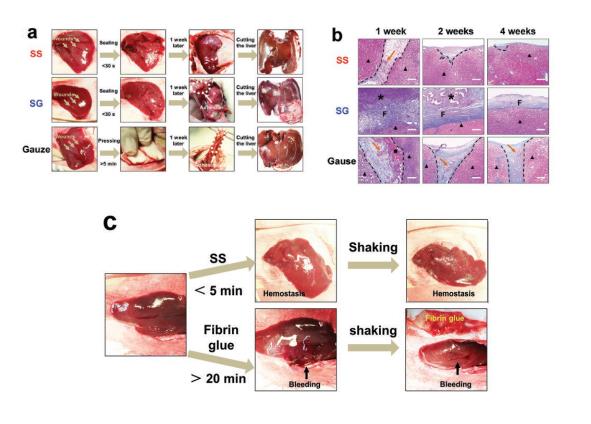
Graphene, as the thinnest, strongest and stiffest material and arranged in a honeycomb pattern structure with sp2-hybridized carbon, finds more potential applications in modern industry than other carbonaceous allotropes; in pristine form, it is also an excellent heat and electric conductor . However, the major obstacle in utilizing graphene, particularly for electronic applications, is its insolubility in the fully reduced state due to the strong affinity between the graphene sheets. In the present study, they synthesized for the first time a polydispersed graphene with desirable electric conductivity by covalent functionalization with single terminal aminated polyethylene glycol monomethyl ether (PEG-NH2). The PEG-NH2 grafted graphene (PEG@GO) was then reduced by hydrazine hydrate to PEG@rGO and subsequently incorporated into epoxy resin by a solution mixing method. The PEG@rGO with a“core-shell”structure exhibited homogeneous dispersion in epoxy and also effectively reduced the dielectric loss, hence contributing excellent dielectric properties and mechanical strength to the final PEG@rGO/epoxy nanocomposites. Fig. 1. Low and high magnification SEM images of (a, a’) neat epoxy, (b, b’) PEG@rGO/epoxy 1.0 wt%, and (c, c’) rGO/epoxy 1.0 wt% nanocomposites. Dielectric properties of PEG@rGO/epoxy nanocomposite. Fig. 1 displays representative SEM images of neat epoxy, PEG@rGO/epoxy and rGO/epoxy nanocomposites. The surface of neat epoxy (Fig. 1a and a') displays a typical smooth structure characteristic of its brittleness. The modified PEG@rGO exhibits excellent dispersion in epoxy (black arrows in Fig. 1b) and no obvious aggregates of PEG@rGO are observed. The magnified SEM image of PEG@rGO/epoxy (see Fig. 1b’) reveals some PEG@rGO nanosheets pulled out or dragged from epoxy and also confirms strong interfacial filler/matrix interaction due to the filler surface functionalization. By contrast, untreated graphene (rGO) nanoplatelets aggregate easily in epoxy matrix caused by the inert surface of reduced graphene as demonstrated in Fig.1c and c', yielding poor mixing and dispersion of rGO. Therefore, the excellent dispersion of PEG@rGO compared to untreated rGO results in enhanced dielectric and mechanical properties of the nanocomposites discussed in the next two sub-sections. Fig. 2. Dispersion state of (a) PEG@GO and (b) PEG@rGO in different solvents after different times. It is known that pristine graphene is extremely insoluble in water and other organic solvents, while GO exhibits polydispersed behavior due to the formation of plenty of hydrophilic oxygen groups. The solubility of PEG@GO and PEG@rGO in different solvents are displayed in Fig.2. As expected, PEG@GO shows good compatibility in water, alcohol, acetone and DMF even after 1 week. The good dispersion of PEG@GO is mainly attributed to the oxygen groups at its edges and basal plane. After reduction, PEG@rGO is less soluble than PEG@GO, especially in alcohol and acetone. ...
View More