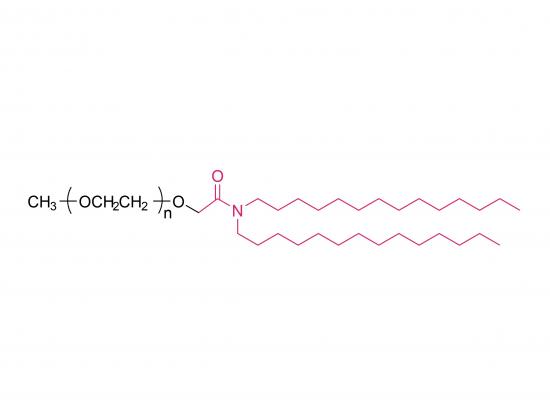
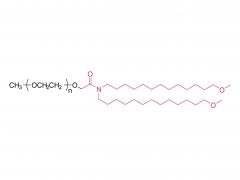
Methoxypoly(ethylene glycol) ditetradecylacetamide
Custom synthesis & CMO services are available.
License is required from license holder.
Has been registered, DMF 038112, CDE F20210000384
SINOPEG is serving pharmaceutical and medical device companies around the globe, with product presence in various pharmaceutical/device development pipeline (pre-clinical, clinical, and post authorization large scale supply). Our facility is ISO9001 and ISO13485 certified, and is operating according to ICH Q7A guidelines to produce products for pharmaceutical companies.
Please contact us at sales@sinopeg.com for PEG derivatives. Our online catalog or inventory may not listed or have all molecular weights and functional groups, which may be available by custom synthesis. Please contact us at sales@sinopeg.com for quotation and availability.
Reference:
1. Nguyen CM, Vu TT, Nguyen MN, et al. Neoantigen-based mRNA vaccine exhibits superior anti-tumor activity compared to synthetic long peptides in an in vivo lung carcinoma model. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2025;74(4):145. Published 2025 Mar 12. doi:10.1007/s00262-025-03992-7
2. Liu S, Wen Y, Shan X, et al. Charge-assisted stabilization of lipid nanoparticles enables inhaled mRNA delivery for mucosal vaccination. Nat Commun. 2024;15(1):9471. Published 2024 Nov 2. doi:10.1038/s41467-024-53914-x
3. Li M, Zheng X, Yu X, et al. Potentiating the Efficacy of mRNA Vaccines through NIR-II Imaging-Guided Precise Vaccination. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025;12(37):e13014. doi:10.1002/advs.202413014
4. Kim S, Jeon JH, Kim M, et al. Innate immune responses against mRNA vaccine promote cellular immunity through IFN-β at the injection site. Nat Commun. 2024;15(1):7226. Published 2024 Aug 27. doi:10.1038/s41467-024-51411-9
5. Liu D, Wang X, Xu L, et al. Screening lipid nanoparticles using DNA barcoding and qPCR. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2025;251:114598. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfb.2025.114598
6. Hassanel DNBP, Pilkington EH, Ju Y, Kent SJ, Pouton CW, Truong NP. Replacing poly(ethylene glycol) with RAFT lipopolymers in mRNA lipid nanoparticle systems for effective gene delivery. Int J Pharm. 2024;665:124695. doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2024.124695
7. Tao Y, Tian C, Qi S, et al. Targeting both death and paracaspase domains of MALT1 with antisense oligonucleotides overcomes resistance to immune-checkpoint inhibitors. Nat Cancer. 2025;6(4):702-717. doi:10.1038/s43018-025-00930-5
8. Yang K, Bai B, Li X, et al. Coordinating interleukin-2 encoding circRNA with immunomodulatory lipid nanoparticles to potentiate cancer immunotherapy. Sci Adv. 2025;11(9):eadn7256. doi:10.1126/sciadv.adn7256
9. Wang Y, Luo G, Wang H, et al. Evaluating cell cycle- and autophagy-associated cellular accumulation of lipid-based nanoparticles. Nat Commun. 2025;16(1):5964. Published 2025 Jul 1. doi:10.1038/s41467-025-60962-4
10. Sui, Meihua & Wang, Yisha & Luo, Gan & Wang, Haiyang & Zheng, Yue & Zhou, Wenbin & Lin, Junrong & Chen, Baocheng. (2024). Construction and Application of a Technical Platform for Determining Cell Cycle- and Autophagy-Associated Cellular Uptake of Lipid-Based Nanoparticles. 10.21203/rs.3.rs-3974581/v1.
11. Wang H, Wang Y, Yuan C, et al. Polyethylene glycol (PEG)-associated immune responses triggered by clinically relevant lipid nanoparticles in rats. NPJ Vaccines. 2023;8(1):169. Published 2023 Nov 2. doi:10.1038/s41541-023-00766-z