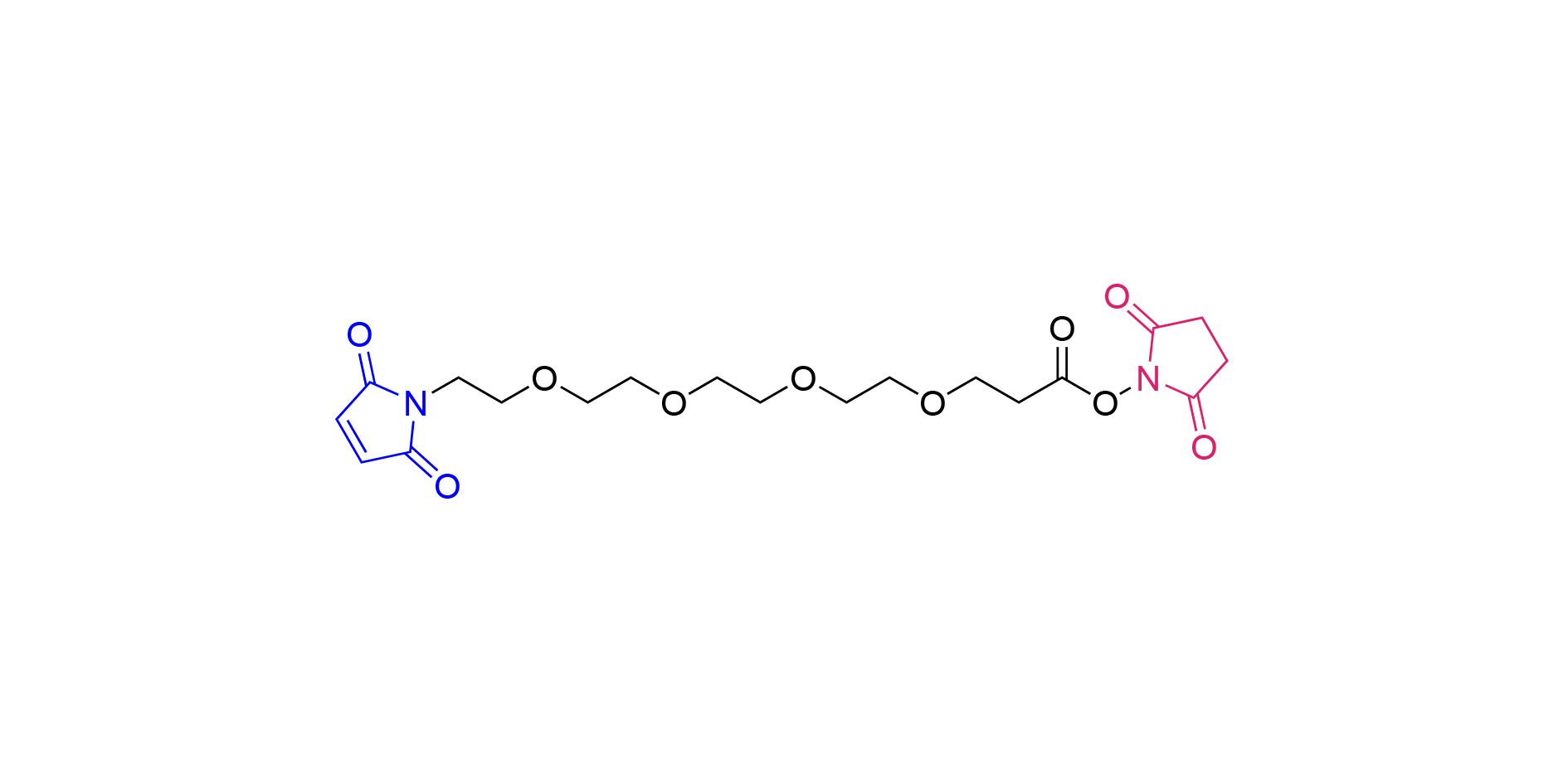
1. Basic information
Name: Maleimide-PEG4-NHS; MAL-PEG4-NHS
CAS number: 1325208-25-0
Molecular formula: C19H26N2O10
Molecular weight: 442.417 (or 442.42, depending on calculation method and accuracy)
2. Structural characteristics
MAL-PEG4-NHS consists of Maleimide, polyethylene glycol (PEG), which contains four glycol units, and n-hydroxysuccinimide (NHS) esters.
Maleimide group: It is a reactive group that can undergo addition reactions with compounds containing sulfhydryl groups (such as proteins, peptides, etc.) to form stable covalent bonds (thioether bonds).
Polyethylene glycol chain (PEG4) : not only increases the water solubility of the compound, but also gives it good biocompatibility. As a non-immunogenic polymer, PEG chains can reduce the non-specific binding between proteins and biological tissues, thus reducing immunogenicity.
N-hydroxysuccinimide (NHS) ester group: gives MAL-PEG4-NHS the ability to react with amine compounds (e.g. primary amines of proteins, amine-modified oligonucleotides, etc.). Under appropriate conditions, NHS ester groups can react with amine groups to form stable amide bonds.
3. Physical properties
Appearance: Usually a grayish white to yellow mixture of solid and liquid, the specific form may vary depending on factors such as purity and storage conditions.
Solubility: Soluble in most organic solvents, such as dimethylformamide (DMF), dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), tetrahydrofuran (THF), etc., but also soluble in water.
Stability: It needs to be stored below -20 ° C and kept dry and away from light. Avoid frequent thawing and repeated freeze-thaw to ensure the stability and activity of the product.
4. Application field
MAL-PEG4-NHS has a wide range of applications in biological coupling and labeling reactions due to its unique structure and properties:
Coupling of biomolecules: Commonly used for labeling and crosslinking of proteins, peptides and nucleic acids. Coupling and labeling between biomolecules can be achieved through the reaction of maleimide groups with sulfhydryl groups, and the reaction of NHS ester groups with amine groups.
Biosensor preparation: Using the coupling function of MAL-PEG4-NHS, biosensors with specific recognition capabilities can be prepared.
Drug development: Used for PEG-modification of drugs to improve drug stability and bioavailability. The introduction of PEG chains into drug molecules through MAL-PEG4-NHS can reduce the immunogenicity and non-specific binding of drugs, thereby improving the efficacy and safety of drugs.
Related recommendations:
| Name | CAS |
|---|---|
| H2N-PEG6-OH | 39160-70-8 |
| H2N-PEG7-OH | 1425973-14-3 |
| H2N-PEG8-OH | 352439-37-3 |
| PA-PEG6-N3 | 361189-66-4 |
| PA-PEG8-N3 | 1214319-92-2 |
| PA-PEG9-N3 | 1670249-37-2 |
| N3-PEG6-OH | 86770-69-6 |
| N3-PEG7-OH | 1274892-60-2 |
| N3-PEG8-OH | 352439-36-2 |
| N3-PEG6-NH2 | 957486-82-7 |
| N3-PEG7-NH2 | 1333154-77-0 |
| N3-PEG8-NH2 | 857891-82-8 |
| HO-PEG6-CO-OtBu | 361189-64-2 |
| HO-PEG8-CO-OtBu | 1334177-84-2 |
| HO-PEG10-CO-OtBu | 778596-26-2 |
| Fmoc-NH-PEG5-CH2COOH | 635287-26-2 |
| Fmoc-NH-PEG6-CH2COOH | 437655-96-4 |
| Fmoc-NH-PEG7-CH2COOH | 152074-20-9 |
| Boc-NH-PEG7-NH2 | 206265-98-7 |
| Boc-NH-PEG9-NH2 | 890091-43-7 |
| Boc-NH-PEG11-NH2 | 890091-42-6 |





















