Engineering PEG-based hydrogels can efficiently foster endothelial network formation in free-swelling and confined microenvironments
Polyethylene glycol (PEG) and its derivatives are among the few polymers approved by the US FDA that can be used in biomedical products. The PEGl-based hydrogel has excellent flexibility and biocompatibility. Some PEG hydrogels can not only be degraded, but also can form bioactive site through modifying the connexins in a chemical way.
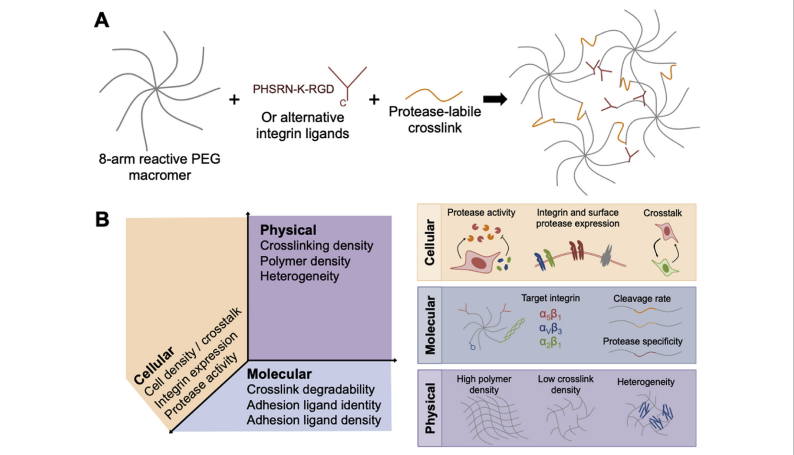
In vitro tissue engineered models are expected to have significant impact on disease modeling and preclinical drug development. Reliable methods to induce microvascular networks in such microphysiological systems are needed to improve the size and physiological function of these models. By systematically engineering several physical and biomolecular properties of the cellular microenvironment (including crosslinking density, polymer density, adhesion ligand concentration, and degradability), the author Alexander Brown establish design principles that describe how synthetic matrix properties influence vascular morphogenesis in modular and tunable hydrogels based on commercial 8-arm poly (ethylene glycol) (PEG8a) macromers. The author applies these design principles to generate endothelial networks that exhibit consistent morphology throughout depths of hydrogel greater than 1 mm.
These PEG8a-based hydrogels have relatively high volumetric swelling ratios (>1.5), which limits their utility in confined environments such as microfluidic devices. To overcome this limitation, the author mitigates swelling by incorporating a highly functional PEG-grafted alpha-helical poly (propargyl-l-glutamate) (PPLGgPEG) macromer along with the canonical 8-arm PEG8a macromer in gel formation. This hydrogel platform supports enhanced endothelial morphogenesis in neutral-swelling environments. Finally, the author incorporates PEG8a-PPLGgPEG gels into microfluidic devices and demonstrates improved diffusion kinetics and microvascular network formation in situ compared to PEG8a-based gels.
[1] Brown A , He H , Trumper E , et al. Engineering PEG-based hydrogels to foster efficient endothelial network formation in free-swelling and confined microenvironments[J]. Biomaterials, 2020, 243:119921.
If there is any copyright infringement, please contact us and we will remove the content at the first time.
Sinopeg provide various NW poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) products: 2KDa, 5KDa, 10KDa, 20KDa, etc.
Products:
Linear Monofunctional PEGs
Linear Bifunctional PEGs
Linear Heterofunctional PEGs
Branched PEGs
Multi-Arm Functional PEGs
Functionally Grafted PEGs





















