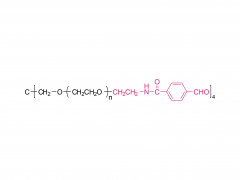
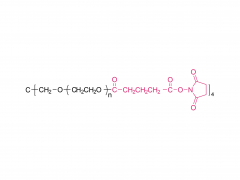
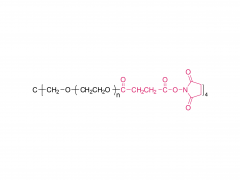
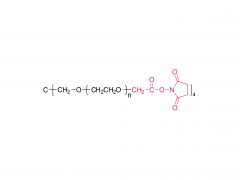
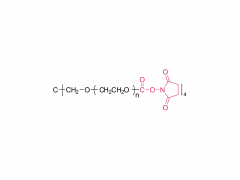
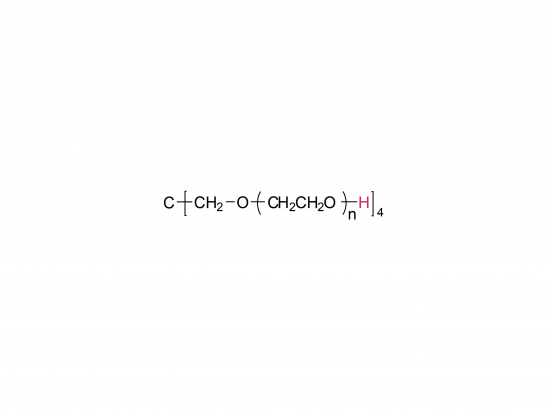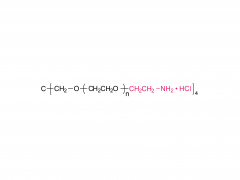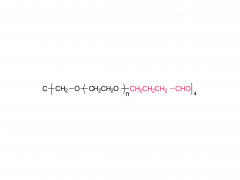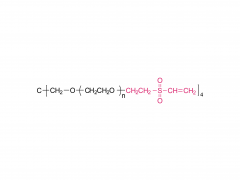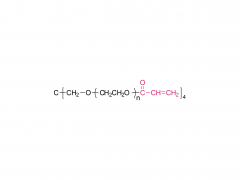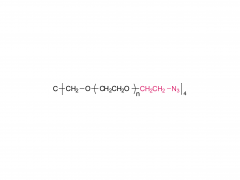4-arm Poly(ethylene glycol)
|
Number |
Mn |
|
06020700102 |
2000 |
|
06020700106 |
5000 |
|
06020700109 |
10000 |
|
06020700112 |
20000 |
|
06020700115 |
40000 |
Xiamen Sinopeg Biotech Co., Ltd. is dedicated to drug delivery systems and related medical device business, focusing on the research, development, production and sales of high-end drug delivery carriers/auxiliary materials/APIs, medical materials, including but not limited to polyethylene glycol derivatives, lipid products, blood sugar control drug modifiers, block copolymers, ADC/ProTAC linkers, biodegradable polymers, exosomes, viral-like particles, as well as providing CDMO and solution services. These products are widely used in long-acting protein/peptide drugs, mRNA vaccines, small nucleic acid drugs, blood sugar control drugs, macromolecular micelle drugs, liposome drugs, gene therapy drugs, immunosuppressants, ADC drugs, ProTAC drugs, medical hydrogels, and other fields, placing the company in a leading position in the industry.
SINOPEG holds 40+ patents, with 80+ more pending, and 30+ products filed in DMF/CDE. The company has ISO 9001/ISO 13485/ISO 14001/ISO 45001 certification. The laboratory and production workshop are designed and built in accordance with the cGMP standard of FDA. We follow the requirements of ICH-Q7A to organize production at scale, to provide high quality drug delivery products and services to customers globally.
Our online catalog or inventory may not listed or have all molecular weights and functional groups, which may be available by custom synthesis. Please contact us at sales@sinopeg.com for quotation and availability.
Reference:
1. Zheng X, Guan S, Zhang C, et al. A Cut-and-Weld Process to 3D Architectures from Multiresponsive Crosslinked Liquid Crystalline Polymers. Small. 2019;15(16):e1900110. doi:10.1002/smll.201900110
2. Li D, Li L, Ma Y, et al. Dopamine-assisted fixation of drug-loaded polymeric multilayers to osteoarticular implants for tuberculosis therapy. Biomater Sci. 2017;5(4):730-740. doi:10.1039/c7bm00042a
3. Wang H, Cheng J, Sun F, et al. A Super Tough, Rapidly Biodegradable, Ultrafast Hemostatic Bioglue. Adv Mater. 2023;35(10):e2208622. doi:10.1002/adma.202208622
4. Pan Z , He G , Xian Y ,et al.Anisotropic Shape‐Memory Cryogel with Oriented Macroporous Channel for Hemorrhage Control and Tissue Generation[J].Advanced Functional Materials, 2025, 35(22).DOI:10.1002/adfm.202422957.
5. Ye J, Chen Y, Deng R, et al. Robust tetra-armed poly (ethylene glycol)-based hydrogel as tissue bioadhesive for the efficient repair of meniscus tears. MedComm. 2024; 5:e738. https://doi.org/10.1002/mco2.738
6. He G, Xian Y, Lin H, et al. An injectable and coagulation-independent Tetra-PEG hydrogel bioadhesive for post-extraction hemostasis and alveolar bone regeneration. Bioact Mater. 2024;37:106-118. Published 2024 Mar 19. doi:10.1016/j.bioactmat.2024.03.015
7. Rui Chen, Xiaojie Yu, et al. Facile synthesis of mechanically robust and injectable tetra-polyethylene glycol/methacrylate chitosan double-network hydrogel cartilage repair, Polymer Testing, Volume 133, 2024, 108410, ISSN 0142-9418, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymertesting.2024.108410.
8. Wei Zhang, Guoke Tang, et al. Fabrication of an injectable hydrogel scaffold embedding kartogenin-encapsulated PLGA microsphere with long-term drug release to promote chondrogenesis, Reactive and Functional Polymers, Volume 196, 2024, 105821, ISSN 1381-5148, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reactfunctpolym.2023.105821.
9. Xue B, Xu Z, Li L, et al. Hydrogels with programmed spatiotemporal mechanical cues for stem cell-assisted bone regeneration. Nat Commun. 2025;16(1):3633. Published 2025 Apr 16. doi:10.1038/s41467-025-59016-6